For men suffering from low testosterone, hormone replacement therapy can be life-changing. But with treatments ranging from weekly injections to implanted pellets lasting months, choosing the right option can be confusing. Shots provide a quick testosterone boost but require frequent doctor’s visits. Pellets avoid the hassle of weekly injections but involve minor surgery for insertion and removal. So which is better: the spike of injections or the steadiness of pellets?
This article breaks down the pros and cons of each method, including side effects, costs, and lifestyle factors. Whether you prefer the routine of shots or the convenience of pellets, read on to discover the best testosterone therapy for you. With the right information, you can take control of low T and start feeling like yourself again.
Importance of Testosterone in Males
Testosterone is an androgen hormone produced mainly in the testicles. It plays key roles in male sexual and reproductive development starting in utero. Throughout puberty, testosterone drives the development of male secondary sex characteristics like facial and body hair growth, deepening of the voice, and muscle development. In adulthood, testosterone maintains libido, sperm production, muscle mass and strength, fat distribution, bone mineral density, and red blood cell production.
Overview of Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
Testosterone production peaks in adolescence and early adulthood, then gradually declines with age. Hypogonadism refers to abnormally low testosterone levels that lead to symptoms like fatigue, low sex drive, erectile dysfunction, and loss of muscle mass.
Hypogonadism can be classified into 2 types:
| Type | Other Names | Possible Causes | Lab Findings |
| 1. Primary Hypogonadism | Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism | Testicular injury, tumor, or infectionGenetic defects affecting testicular development (e.g. Klinefelter syndrome)Chemotherapy, radiation treatment, alcohol abuse | Low serum testosterone, high LH and FSH |
| 2. Secondary Hypogonadism | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism | Hypothalamic or pituitary disordersInflammatory diseasesKallmann’s syndromeObesityAgingHIV/AIDS | Low testosterone, normal to low LH and FSH |
Hypogonadal Symptoms, Levels, and Effects
Symptoms of low testosterone may include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, depression, irritability, loss of muscle mass and strength, increased body fat, and diminished work performance. Diagnosis is made if total serum testosterone level is below 300 ng/dL or free testosterone is below 5-9 pg/mL.
TRT aims to raise serum testosterone into mid-normal range (400-700 ng/dL) to resolve symptoms. Dramatic effects are not seen, but most men report improved energy, mood, libido, muscle mass, body composition, and quality of life.
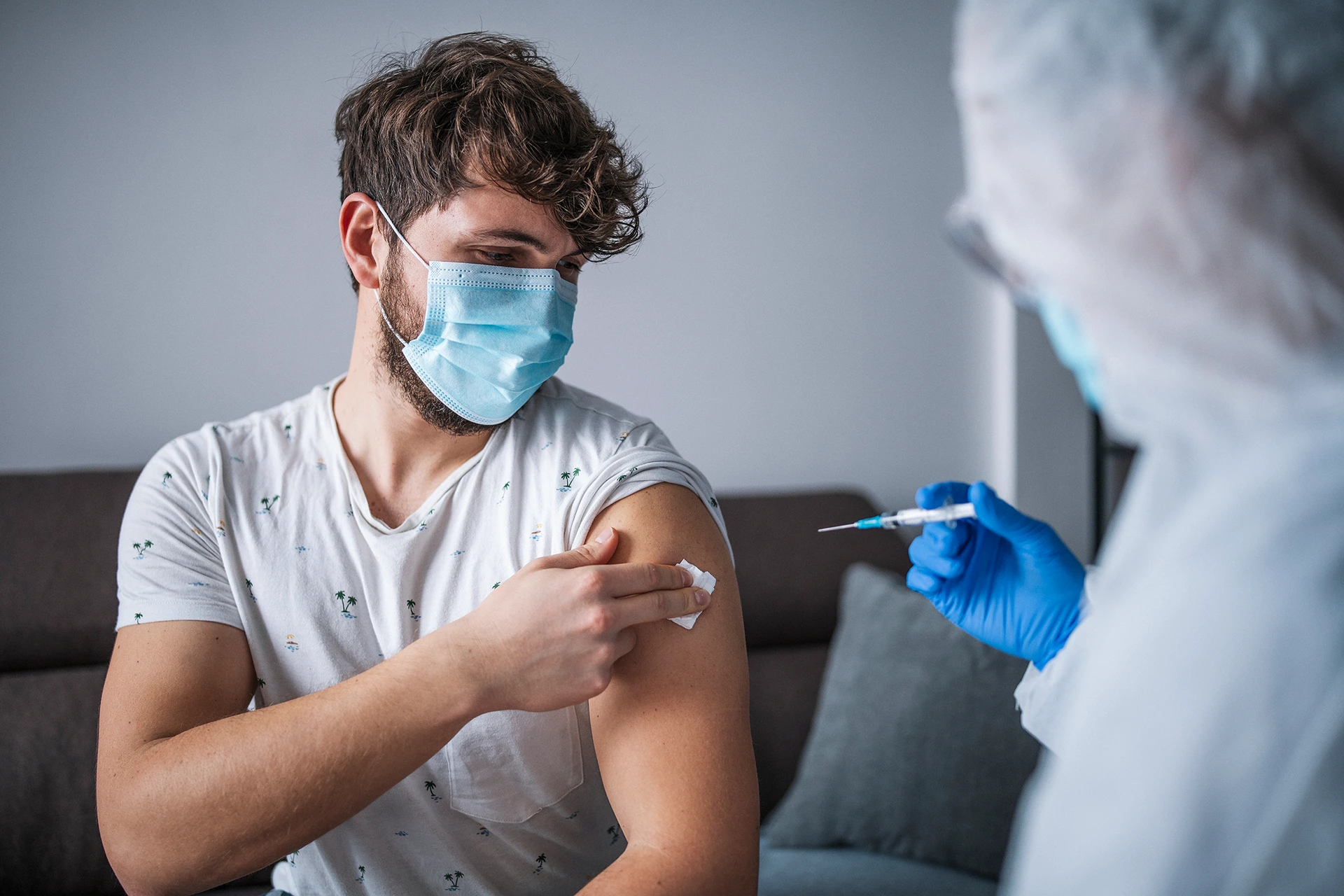
Administration Methods: Injections vs. Pellets
Testosterone replacement therapy can be administered through intramuscular injections and subcutaneous pellets.
1. Intramuscular Injection
Testosterone injections, typically testosterone cypionate or enanthate, are given intramuscularly into the gluteal muscle or thigh. Doses range from 50-400 mg every 1-4 weeks. Levels peak within 1-3 days then decline until the next injection.
Frequent injections are needed to maintain stable blood levels. Side effects may include pain, swelling, bruising, bleeding, or infection at the injection site.
2. Testosterone Pellets
Testosterone pellets are implanted subcutaneously, typically in the hip or buttocks. Pellets are 2-6mm long cylinders that contain crystalline testosterone. Around 10-15 pellets containing 75-150 mg testosterone are implanted at once under local anesthesia. They dissolve slowly, releasing testosterone steadily over 3-6 months.
Pellet insertion involves a minor surgical procedure but avoids the peaks and valleys of injections. Potential side effects include infection, pellet extrusion, bruising, and scar tissue formation.
Comparison
| Feature | Testosterone Injections | Testosterone Pellets |
| Dosing | Single large dose absorbed quickly | Smaller doses from multiple pellets |
| Testosterone levels | Peak after injection then drop until next injection | Steadier levels over months |
| Administration | Frequent injections in doctor’s office | Minor surgical procedure to implant pellets every 4-6 months |
| Patient considerations | Frequent doctor visits for injections | Periodic minor surgical procedures for pellet implantation |
Hormone Levels & Monitoring

Ongoing monitoring of testosterone and other hormone levels is important for evaluating treatment efficacy and safety. Baseline testosterone, estradiol, prolactin, and PSA levels should be measured before starting TRT and should be rechecked periodically during treatment. The goal is to raise testosterone levels into the mid-normal range while minimizing side effects. Comparing current to baseline hormone levels helps determine appropriate testosterone dosing.
TRT often lowers HDL (“good”) cholesterol by 5-10% while raising LDL (“bad”) cholesterol by 5-15%. Elevated hematocrit is also common. Periodic bloodwork monitors these parameters to ensure safety. TRT likely increases the risk of adverse cardiovascular events in men already at risk for heart disease.
Blood Tests and Their Key Role
Frequent blood work is needed to monitor testosterone, estradiol, hematocrit, PSA, and lipids. Testosterone should be assessed midway between doses. Estradiol levels may rise due to peripheral conversion of testosterone to estrogen. Every 3-6 months, lipids, PSA, and hematocrit should be checked. Dose adjustments can be made based on results.
Benefits of Testosterone Therapy
When properly administered, testosterone therapy can provide a wide range of benefits including:
| Benefits | |
| Improved energy levels | TRT can increase vigor, reduce fatigue, and restore normal energy levels in men with low testosterone. This allows them to be more active and engaged in daily activities. |
| Increased libido | TRT helps normalize testosterone levels, which can increase libido, sexual desire, arousal, and overall sexual function. Men report improved sexual activity, more satisfying orgasms, and better erections. |
| Improved mood | TRT can greatly improve mood, reduce depressive symptoms, and enhance overall mental wellbeing in men with low testosterone. Men often feel less agitated, more motivated, and have an improved sense of wellbeing. |
| Increased muscle mass and bone density | TRT helps stimulate muscle growth, increases lean muscle mass, strengthens bones, and reduces risk of osteoporosis and fractures in men with low testosterone. This provides greater strength and reduces frailty. |
| Improved cognitive function | TRT can sharpen focus, improve memory, enhance visuospatial skills, and quicken processing speed in men with low testosterone. This leads to better executive functioning and clearer thought processes. |
Cost of Testosterone Injections vs. Cost of Testosterone Pellet
Testosterone injections are generally the most affordable option for TRT, while pellets are more costly.
Testosterone injections cost $150-300 for a 10ml vial, lasting 2-3 months. Pellets cost $350-650 for the insertion procedure plus $40-100 per pellet. Given the need for re-implantation every 4-6 months, annual pellet costs can approach $2000 vs. $600 for injections. However, pellets avoid frequent office visits for injections.
While pellets come with a higher upfront cost, some patients feel their benefits justify the expense. More stable hormone levels, less time in doctors’ offices, and steadier symptom relief promote treatment adherence. This long-term value may outweigh the direct cost difference for some men.
Other Considerations
1. Body Composition Parameters: Muscle Strength, Body Mass, Body Weight
Overweight men tend to aromatize more testosterone to estrogen and may benefit from smaller, more frequent testosterone doses. Highly muscular men may need larger or more frequent doses to maintain mass. Adjustments cater to individual body composition.
2. Influence of Diet on Lipid Parameters
Diet significantly affects cholesterol levels. TRT patients whose lipid profiles worsen should receive dietary counseling for reducing saturated fats, simple carbohydrates, and trans fats, while increasing healthy fats, fiber, and complex carbohydrates. This can counteract TRT-induced lipid changes without needing to adjust the testosterone dose.
3. Influence of TTh and Lack of Influence on Various Parameters
Transdermal testosterone therapy methods such as gels and creams can help normalize testosterone levels without significantly affecting hematocrit, hemoglobin, or lipids. However, skin reactions are common. For patients who want to avoid injectable or pellet therapy, transdermal preparations provide an alternative without influencing circulatory parameters.
4. Personal Preferences
For those wanting infrequent doctor visits may prefer pellets over injections. Patients averse to surgery may opt for gels or injections instead. Cost, pharmacokinetics, and side effect profile must be weighed according to individual preferences. Shared decision-making optimizes adherence and outcomes.
Safety and Medical Concerns
While generally safe when properly monitored, testosterone therapy has some risks to consider.
- Risk of Infection: Both pellet implantation and injections carry a low risk of infection, bleeding, or reaction to local anesthetic, following sterile techniques. While uncommon, these risks should be discussed to ensure your safety.
- Contraindications: TRT should be used cautiously in men with significantly enlarged prostates. It may be contraindicated after radical prostatectomy given lack of data. Discuss the risks and benefits with a urologist.
- Increased hemoglobin and hematocrit: TRT can increase red blood cell mass and hemoglobin or hematocrit levels. This may require periodic blood donation to avoid complications.
- Liver toxicity: Use of oral testosterone formulations may rarely cause liver inflammation or damage. Injections and pellets avoid this issue. Liver tests should be monitored periodically.
- Sleep apnea worsening: Men with sleep apnea may experience worsening symptoms on TRT. Sleep studies before and during treatment can identify this issue.
Final Thoughts
While TRT provides benefits, variations in response make definitive conclusions elusive. Still, increased recognition of hypogonadism in aging men enables individualized treatment that improves quality of life. Patients should be informed of all therapeutic options through shared decision-making.
The choice between testosterone injections and pellets must be made carefully through shared decision-making between patient and provider. There is no one-size-fits-all approach to TRT. The best option depends on patients’ preferences, anatomy, comorbidities, and metabolism. Pellet placement is easier in lean men, while frequent injections work better for some obese men. Personalization optimizes outcomes.
Physician’s Rejuvenation Centers’ Approach to Hormone Therapy
At Physician’s Rejuvenation Centers, we offer effective testosterone replacement therapy to help you reclaim your energy, strength, and passion. Skipping injections and opting for long-lasting pellets can steady your testosterone levels for months at a time. Or choose injections for affordable testosterone boosts on your own schedule.
Our expert physicians will work with you to create a customized low testosterone treatment plan to fit your lifestyle and preferences. Regular follow-ups and blood work ensure your safety and optimal results.
Don’t let low T sap your vitality any longer. Contact Physician’s Rejuvenation Centers today to learn more about injectables, pellets, and other proven testosterone therapies. It’s time to start feeling like yourself again.