Navigating the Process: Safely Discontinuing Testosterone Therapy and Managing Withdrawal Symptoms
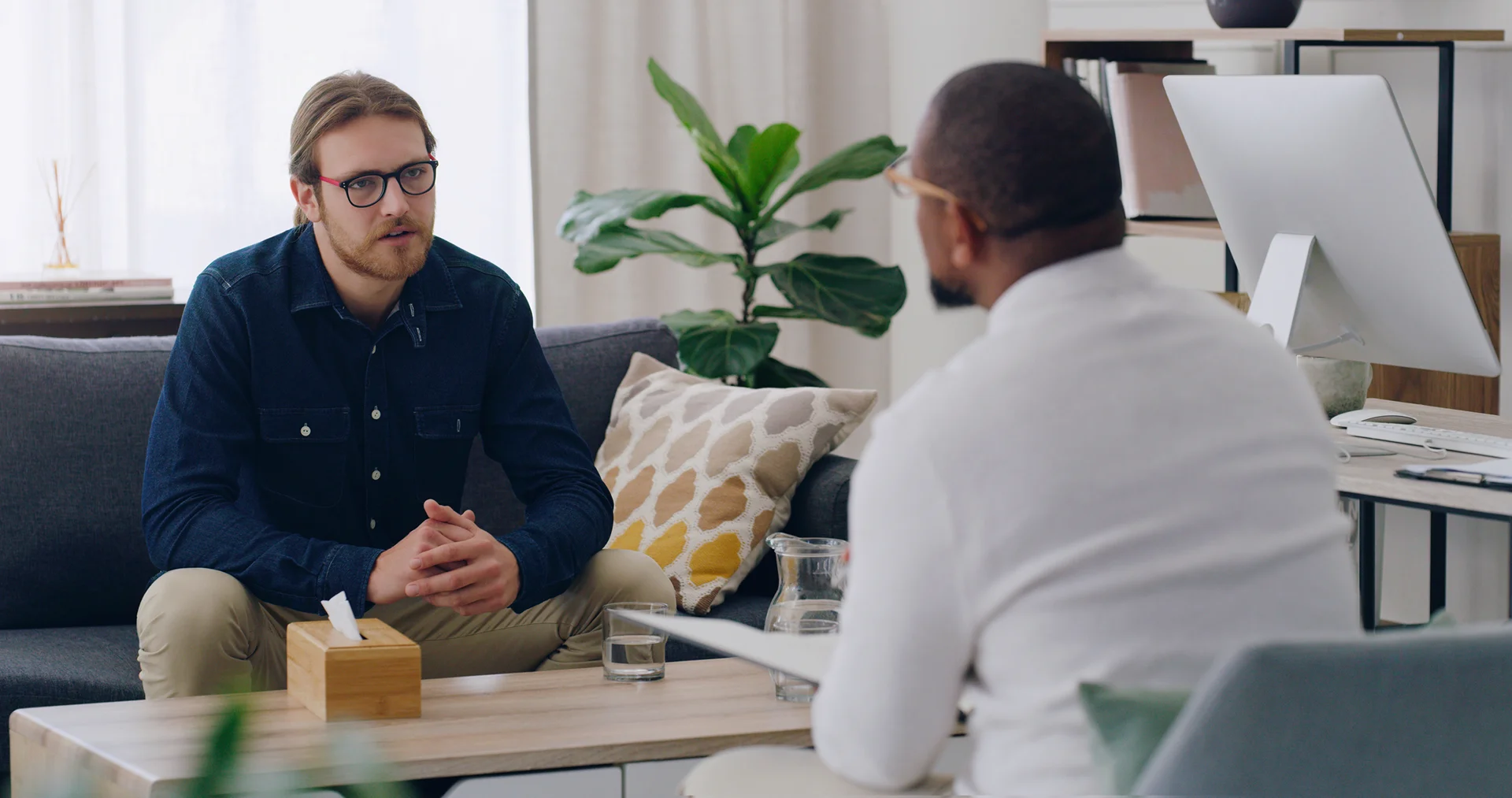
You’ve been on testosterone for some time now and feeling pretty good, but you’re starting to wonder if you really need it anymore. Your doctor said there’s only one way to find out – it’s time to stop the treatment and see how your symptoms change. However, stopping testosterone therapy, also known as hormone replacement or augmentation, is not as simple as just quitting cold turkey.
Coming off testosterone differs from simply discontinuing replacement therapy. When you’re on replacement T, your body has stopped producing its own testosterone, so stopping the medication abruptly can lead to low T symptoms returning quickly. The medical experts recommend gradually tapering your dosage to allow your body’s natural testosterone production to resume itself. This process, known as hormone withdrawal or therapy cessation, needs to be done under medical supervision to minimize side effects.
What Are the Key Factors To Consider When Discontinuing Testosterone Therapy?
| Important Factors for Stopping TRT | Description |
| Dosage tapering | Slowly decrease dosage over time, reducing the amount by 10-25% every few weeks. Allows the body to adjust and avoid severe withdrawal symptoms. |
| Symptom monitoring | Pay close attention to returning symptoms like fatigue, depression, muscle loss, etc. Promptly report them to your doctor for possible treatment plan adjustments. |
| Lifestyle changes | Exercise, diet, stress reduction, and adequate sleep can help boost natural T production and make the transition off hormones smoother. |
| Alternative treatments | Other medications or therapies like clopidogrel, pralmorelin, or testosterone pellet implants may be prescribed to manage symptoms during the transition. |
| Homeostasis return | It can take several months for the body’s natural testosterone levels and regulation to stabilize after stopping TRT completely. Blood tests will confirm hormone levels have balanced out. |
| Follow-up care | Regular follow-up appointments with the doctor are critical, especially in the first year after stopping TRT. Monitoring for any return of symptoms or other issues is important for long-term health and well-being off of testosterone therapy. |
Are There Any Complications Associated With Discontinuing Testosterone Therapy Abruptly?
Yes, abruptly stopping testosterone therapy can lead to several complications. Some potential issues include:
Testosterone withdrawal: Stopping testosterone medication suddenly can cause severe low T symptoms to return quickly like fatigue, low libido, depression, and muscle loss. This is known as testosterone withdrawal and should be avoided. Gradual dosage tapering is the safest approach.
Hypogonadism recurrence: If you have primary or secondary hypogonadism, abruptly stopping T will likely cause your condition to recur, resulting in very low or no testosterone production again. This could require restarting treatment to manage symptoms.
Infertility: Stopping testosterone abruptly can impact sperm production and fertility in men, at least temporarily. For those hoping to conceive a child naturally, it’s best to discontinue T under medical guidance.
Prostate growth: Testosterone helps stimulate prostate growth, so stopping too quickly could allow the prostate to become large again, increasing risks like BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia) or prostate cancer.
Mood changes: Rapid cessation of testosterone can trigger depression, anxiety, irritability, and other mood or mental health issues in some men due to the loss of T’s mood-supporting effects. Gradual tapering helps avoid severe mood swings.
Bone loss: Testosterone helps maintain bone mineral density and strength. Abruptly stopping T could lead to increased bone loss and osteoporosis risk over time without proper preventative treatment or alternatives. Calcium, vitamin D, weight-bearing exercise, and bisphosphonates may be recommended.
Fat gain: Testosterone influences metabolism and loss of lean muscle mass. Stopping too quickly could allow fat gain as muscle is lost and metabolism decreases. Diet and exercise are even more critical during this transition.
In summary, it’s best to discontinue testosterone therapy under medical supervision using a gradual dosage taper. This approach helps minimize risks and ensure a smoother transition with fewer complications.
What Is the Recommended Protocol for Stopping Testosterone Replacement Therapy Safely?

To safely and effectively stop testosterone replacement therapy, it’s critical to follow the recommended medical protocol. Here are the key steps:
First, schedule an appointment with your prescribing doctor to discuss stopping testosterone. Bring all your medications, dosages, administration details, and any concerns you have. Your doctor will determine if it’s appropriate and safe to discontinue treatment at your current time. If so, they will instruct you on the proper dosage tapering schedule to follow.
Typically, testosterone levels will be checked through blood tests to determine where you stand currently. From there, your doctor will provide a dosage schedule to reduce the amount by a specific percentage, often around 10-25% every few weeks. This allows your body to adjust slowly to decreasing T levels and minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Don’t decide to stop “cold turkey” on your own. Always work with your doctor on adjustments to your treatment plan. As you decrease your dosage, continue to monitor how you feel and watch for any concerning symptoms. Be ready to report them promptly to make additional changes if needed. Some men may need to stay at a stable lower dose for a while before continuing to taper down.
Once you’ve stopped testosterone injections or patches completely, it can take 3 months or longer for your natural T levels and regulation to stabilize again. Follow-up blood tests and appointments with your doctor will confirm when it’s safe to consider yourself “off” testosterone completely. Continue with lifestyle recommendations like exercise, diet changes, and stress reduction during this time.
Supplements or alternative treatments may be suggested to help boost T production or manage symptoms. Oral testosterone tablets or testosterone pellets can also potentially be used temporarily if needed. The most important things are patience, commitment to the process, and vigilance with follow-up care.
Stopping testosterone therapy is a big step, so take your time to prepare and feel fully ready. Ask any questions you have to feel completely confident in the plan provided by your doctor. You’ve got this! By following the recommended protocol and guidelines, you can successfully and safely stop testosterone replacement treatment.
How Can One Effectively Wean Themselves off of Testosterone Replacement Therapy?
Several effective strategies can help make weaning off testosterone replacement therapy easier and smoother. Some key methods include:
Gradual dosage tapering: The most important first step is following your doctor’s recommended schedule for slowly decreasing your T dosage over time. Typically reducing the amount by 10-25% every 2-4 weeks is a safe approach, but again work closely with your doctor to develop a tapering schedule specific to your needs and treatment.
Are There Any Specific Methods, Such as Using Hcg, To Help Get Off Testosterone Therapy More Smoothly?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) therapy may be recommended to help restart your body’s natural testosterone production before stopping replacement T completely. hCG mimics the luteinizing hormone that stimulates testosterone release from the Leydig cells in the testes. Dosing hCG while tapering off testosterone can help energize testosterone production and minimize symptoms during withdrawal.
Supplements and herbs: Certain supplements like DHEA, zinc, vitamin D, and ashwagandha may provide a natural boost in testosterone levels and support adrenal and gonadal function. DHEA in particular could help reactivate your body’s ability to produce testosterone on its own again. However, always check with your doctor first before taking any new supplements to ensure there are no interactions with your current treatment.
Lifestyle improvements: Exercise, diet, stress reduction, and sleep are essential for hormone health and balance. Engage in regular cardiovascular exercise or high-intensity interval training, follow a whole foods diet with lean protein and healthy fats, practice meditation/yoga, limit alcohol/caffeine, and aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night. These natural strategies will help keep your energy and mood high while stopping testosterone.
Consider topical testosterone: For some men, applying testosterone creams or gels directly to the skin may provide enough supplemental T without the risks of injections or patches. Using a lower dose topical formula while tapering off injections could help ease symptoms as production restarts. But again, medical supervision is important for this approach.
Be patient through fluctuations: Stopping testosterone will likely cause your levels and symptoms to fluctuate for a period of months. Some days may feel worse than others. Remain committed to your plan and be willing to make adjustments as needed under doctor’s guidance. Levels will start to stabilize over time.
What Are the Potential Side Effects of Stopping Testosterone Therapy?
Stopping testosterone therapy, whether abruptly or gradually, can potentially lead to several side effects. Some common issues include:
Testosterone withdrawal: Stopping T treatment leads to decreasing testosterone levels in the body. This can cause low T symptoms like fatigue, decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction, depression, and muscle loss to return. Testosterone withdrawal is unavoidable when stopping T, but following a taper schedule can minimize severity.
Infertility: Testosterone supports sperm production in men, so stopping T may cause temporary or permanent infertility depending on the individual and duration/dose of treatment. If hoping to conceive naturally in the future, medical guidance on cessation is especially important.
Changes in mood: Testosterone influences mood, stress response, and mental well-being. Stopping T can trigger issues like depression, anxiety, irritability, and even mania in some men. Proper dosage tapering and follow-up care can help prevent severe mood changes, but side effects are still possible.
Bone loss: Testosterone prevents bone loss and maintains bone density. Stopping treatment could allow for decreases in bone mass, increasing risks of osteoporosis or more fragile bones over time without preventative treatment. Calcium, vitamin D, weight-bearing exercise, and bone-supportive medications may be recommended based on duration of T use.
Increased estrogens: When testosterone levels drop due to stopping treatment, the body may compensate by increasing estrogen production. This can lead to weight gain/fat accumulation, gynecomastia (breasts), and changes in cholesterol/heart health. Avoiding drastic leaps and bounds in hormone levels is important.
Metabolic changes: Testosterone influences how the body processes energy and builds muscle/bone. Sudden stoppage can trigger unwanted changes like increased appetite, weight gain, impaired endurance, and loss of muscle mass. Gradual cessation and lifestyle modifications are critical to minimize these metabolic side effects.
Sleep changes: Testosterone supports sleep and wakefulness cycles. Stopping T has the potential to lead to sleep quality issues, fatigue, and even sleep disorders without proper management. Practicing good sleep hygiene, limiting screen time before bed, and using over-the-counter aids may help in some cases. Medical treatment may be needed for severe symptoms.
What Withdrawal Symptoms Might One Experience When Getting off Testosterone Replacement Therapy?
Common withdrawal symptoms experienced when stopping testosterone replacement therapy include:
Fatigue and low energy: Testosterone supports stamina and vitality, so decreasing T levels often lead to feelings of tiredness, sluggishness and low endurance.
Decreased sex drive: Testosterone stimulates libido, so dropping T typically results in a lowered interest in sex and reduced erectile function.
Depression or mood changes: Testosterone influences mood and well-being. Stopping T can trigger issues like depression, anxiety, irritability, and changes in cognition or mental clarity.
Muscle loss: Testosterone builds muscle mass and strength. As T levels drop from stopping treatment, loss of muscle tone and definition is common. Some muscle atrophy can even occur without proper management.
Changes in body composition: Decreasing testosterone often leads to loss of muscle and increase in body fat. This can result in a less athletic build and weight gain, especially around the midsection.
Infertility concerns: If you stop testosterone in hopes of naturally conceiving a child, sperm production and fertility could temporarily or permanently decrease due to changes in hormone levels. It’s best to discuss fertility plans with your doctor before stopping T.
Decreased libido: Lower testosterone typically equates to a reduced interest in sex and decreased frequency/intensity of arousal or orgasm.
Sleep disturbances: Testosterone helps regulate sleep-wake cycles, so changes in hormone levels at night can lead to issues like insomnia, restlessness, and sleep disorders.
Hair loss: For those prone to male pattern baldness, further hair thinning or even hair loss is possible when testosterone production or medication is interrupted. Hair often regrows once hormone levels stabilize again.
Sweat changes: Fluctuations in T may trigger either increased or decreased sweating for some individuals. Night sweats, excessive day sweating or lack of sweating could occur. Sweat production usually regulates again over time.
Acne: Clogged pores and breakouts are possible during periods of rapid hormone change. However, acne is not inevitable and depends on skin type and T level fluctuations. Let your dermatologist know about any changes in treatment.
How Long Does It Take for the Body To Recover and Start Producing Testosterone Naturally After Stopping Therapy?
Recovery of natural testosterone production: On average, it can take 3 to 6 months for the body to fully recover testosterone levels and regulation after stopping replacement therapy. However, this time period varies from person to person based on factors like:
- Duration of treatment: Longer treatment duration means the body has had more time to stop producing its own testosterone, extending recovery time.
- Underlying condition: Issues like primary vs secondary hypogonadism impact how quickly the body can rebound testosterone production.
- Patient age and health: Overall health, weight, metabolism and age can influence the body’s ability to restore testosterone levels naturally after stopping treatment.
Follow-up testing with your doctor, including blood work and symptom review, is needed to confirm when testosterone levels have stabilized in the normal range again and it’s considered fully recovered.
What Are the Health Effects of Stopping Testosterone Replacement Therapy, and How Can They Be Managed?
By following the recommended medical protocol for stopping testosterone, staying committed to lifestyle changes, monitoring for symptoms, and prompt reporting of issues, the potential health impacts can be managed effectively. But some side effects may continue for a period of months even after hormone recovery. Close follow-up with your doctor is critical, especially in the first year after stopping treatment.
| Risks and Concerns of Low T and TRT | Description |
| Testosterone deficiency | Risk of developing low T symptoms like fatigue, depression, erectile dysfunction, and loss of muscle/bone mass. Management includes dosage tapering, lifestyle changes, and possibly supplemental treatment. |
| Infertility concerns | Changes in hormone levels may cause temporary or permanent issues with sperm production and fertility. Discuss plans with a urologist before stopping TRT if conception is a goal. |
| Metabolic changes | Altered metabolism, weight gain/loss, and changes in cholesterol may occur due to hormone fluctuation. Adjust diet and exercise under medical guidance. |
| Mood changes | Issues with depression, anxiety, irritability, or mania are possible. Tapering schedule, supplements, therapy, and medication may help manage symptoms. |
| Bone health decline | Without preventative care like calcium/vitamin D and weight-bearing exercise, bone loss and osteoporosis risk increase. Severe impacts may require bisphosphonates or other treatment. |
| Sleep disturbances | Changing hormone levels can disrupt sleep-wake cycles leading to insomnia, fatigue, or other sleep issues. Practice good sleep hygiene and use over-the-counter aids as recommended. Severe cases may require medical treatment. |
Take control of your health journey with the expert guidance from Physicians Rejuvenation Centers
Schedule a consultation today and let our specialists help you navigate the process of safely discontinuing testosterone therapy while managing withdrawal symptoms.