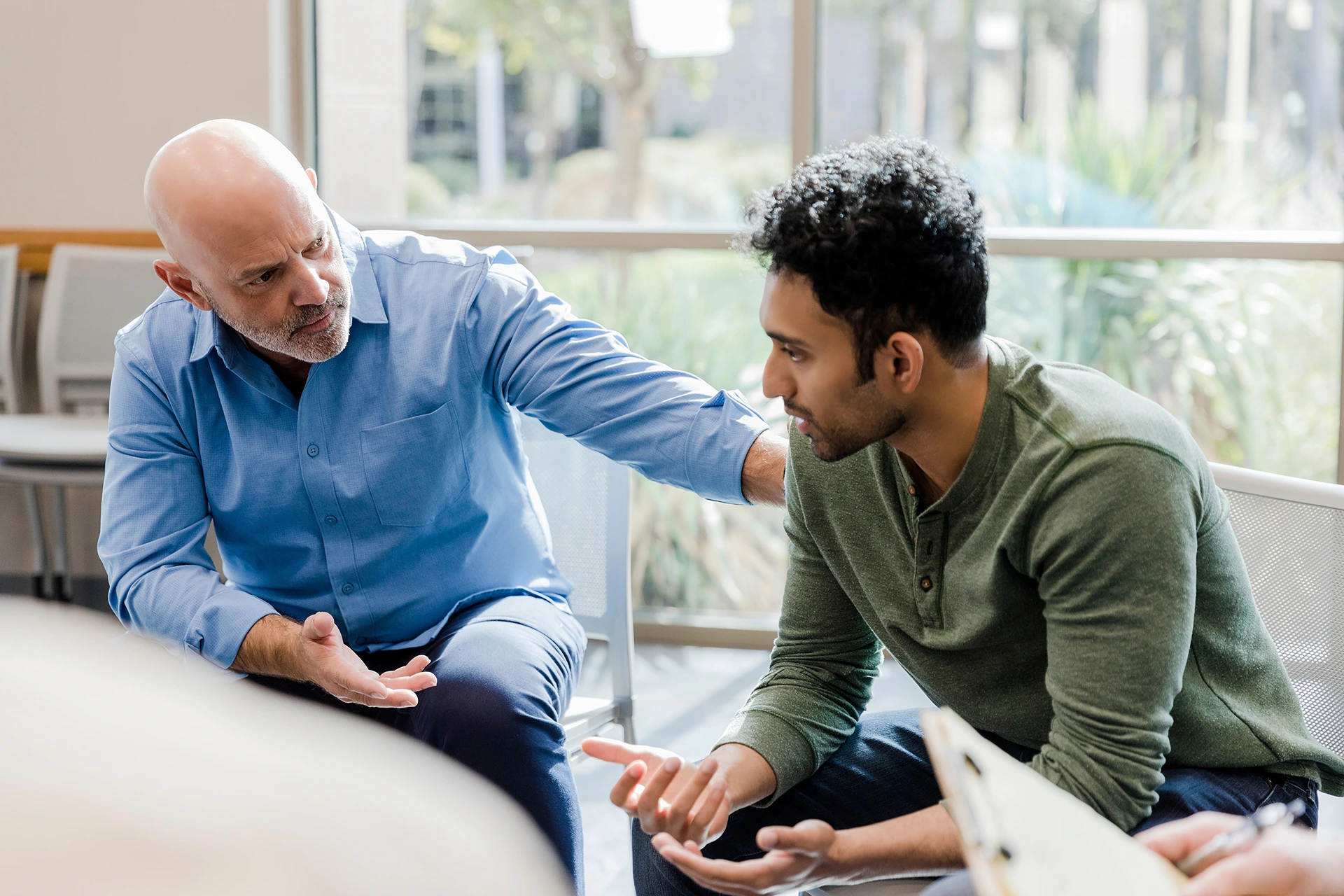
A Safe Alternative to Treating Low T Symptoms
As we age, our hormone levels naturally decline which can impact our quality of life. If you’ve been experiencing bothersome symptoms of low testosterone, bioidentical hormone replacement therapy may provide relief.
This article will explore how BHRT works and its potential benefits.
What is Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy (BHRT)
Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy, commonly referred to as BHRT, involves restoring hormone levels to their optimal ranges through the administration of hormonal preparations that are chemically identical to the hormones naturally produced by the human body.
Specifically, compounded bioidentical hormones are designed to match a person’s individual biological needs based on salivary testing and other diagnostic methods. These customized preparations aim to avoid adverse impacts while still providing necessary symptom relief.
Importance of Hormones in the Human Body
Hormones play critical regulatory roles throughout the human lifespan. As endogenous biochemicals produced by the endocrine system, they control vital processes like metabolism, mood, cognition, immunity, bodily functions, cardiovascular health, bone strength, lean muscle mass, and reproductive function.
During the menopausal transition and beyond, fluctuations in estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and other hormones can negatively impact homeostasis in women. Strategic hormone supplementation seeks to maintain well-being by supporting the body’s normal physiological pathways and mechanisms.
Transitioning through various hormonal stages smoothly impacts long-term health and quality of life. Keeping levels optimized is paramount for general wellness into the post-menopausal decades.
Understanding Hormones
Endogenous hormones, also called human hormones, are biochemicals generated within the endocrine glands including the ovaries, testes, thyroid, pancreas, and adrenal cortex. Each secretion delivers coordinated chemical messages to direct metabolic processes, cellular activities, tissue functionality, and organ system operations throughout the organic system. Nature designed these body-identical substances to interface on a molecular stage directing homeostatic homeostasis.
Natural Hormones and Synthetic Hormones
Our bodies make their own hormones to regulate important functions. These natural hormones have very specific molecular structures that are perfectly matched to our biology.
Synthetic hormones are made in laboratories and are meant to mimic the effects of natural hormones. However, they are not identical copies. Their molecular makeup is slightly different than what our bodies produce.
Some examples of synthetic hormones include birth control pills and hormone replacement therapies. While these can help replace hormones when our bodies don’t make enough, their non-identical structure means they may not interact with our cells in exactly the same way as natural hormones.
Bioidentical Hormones vs. Man-made Hormones
Bioidentical hormones and synthetic hormones are both used in hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to alleviate symptoms of menopause. Here are their key differences:
| Type | Source & Composition | Molecular Structure | Production |
| Bioidentical Hormones | Made from plant sources such as yams and soy | Have the same molecular structure as the hormones made by the human body | Can be produced by a pharmaceutical company or a compounding pharmacy |
| Synthetic Hormones | Made from man-made chemical compounds | Do not have the same molecular structure as the hormones in the human body, but the body can convert them into a usable form | Can never match the complexity of a natural hormone |
Types of Hormone Therapies

1. Traditional Hormone Therapy
Traditional hormone therapy refers to the use of prescription hormonal medications, typically estrogen alone or estrogen in combination with progestogen, to restore declining hormone levels in women experiencing menopause. It has been used since the 1950s and 1960s to treat menopausal symptoms. The estrogens most commonly prescribed in traditional hormone therapy are conjugated estrogens, which can be equine (CEE) or synthetic, as well as micronized 17β estradiol and ethinyl estradiol.
2. Bioidentical Hormone Therapies
Bioidentical hormone therapies refer to the use of hormones that have the same chemical and molecular structure as hormones naturally produced in the human body. These hormones can be derived from plant sources and are processed to mimic the hormones made by the body’s glands. Bioidentical hormones can include commercially available products approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), such as micronized progesterone and estradiol, as well as compounded preparations.
There are different forms of BHRT. These are:
| Form | Description |
| Oral bioidentical hormone therapy | This involves taking bioidentical hormones in pill form. The hormones can be taken alone or in combination with other hormones, such as progesterone. |
| Transdermal bioidentical hormone therapy | This involves applying bioidentical hormones to the skin using patches, gels, or creams. The hormones are absorbed through the skin and into the bloodstream. |
| Bioidentical hormone pellet therapy | This involves inserting small pellets containing bioidentical hormones under the skin. The pellets release hormones into the bloodstream over time. |
| Bioidentical hormone injections | This involves injecting bioidentical hormones directly into the muscle or under the skin. The hormones are absorbed into the bloodstream and can provide long-lasting effects. |
Importance of Individualized Doses and Consistent Dose
It is important for bioidentical hormone replacement therapy to use individualized doses and maintain a consistent dose for each patient. Due to variances in hormone levels, symptoms, medical histories, and genetics between patients, an individualized dosing approach is necessary. Finding the proper individualized dose and administering it consistently can effectively manage symptoms by tailoring the hormone therapy to each unique patient’s needs.
Menopause and Hormonal Imbalance
As the process of menopause advances in a woman’s body, signs and feelings associated with fluctuating estrogen and other hormone concentrations may arise. Some commonly experienced phenomena include:
- Increased body temperature, sweating, and heart rate during “hot flashes”
- Decreased natural lubrication of vaginal tissues causing discomfort
- Alterations in fat and muscle distribution lead to shifts in body weight and form
- Sensations of emotional lability and mood variations at unexpected times
Estrogen and Testosterone in Menopause
Estrogen and testosterone play pivotal regulatory roles in multiple physiological systems throughout a woman’s lifetime. As levels of these key hormones drop during the menopausal transition, homeostasis can become threatened in processes reliant upon their balancing presence. Disruptions in typical functioning then bring on disruptive changes felt both internally and externally.
As natural aging moves women past their reproductive years, stability and harmony in realms steadily modulated by ovarian hormones grow ever more important. Symptoms arise when imbalance takes hold in sensitive domains previously held steady. Supporting well-being and quality of life in this phase demands thorough comprehension of the perplexing intricacies by which the deepest female rhythms were once kept steady.
Testosterone and BHRT
Restoring levels with bioidentical hormone substitution treatment can turn around age-related decay and improve personal satisfaction. BHRT advances testosterone to more youthful, solid ranges, enhancing the quality of life and expanding dangers for conditions like osteoporosis. It is a sheltered, successful choice for those needing mitigation from indications of a drop in testosterone.
The Science Behind BHRT
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy restores testosterone levels in men through the use of bioidentical testosterone supplements that are chemically identical to the body’s natural testosterone.
When administered through topical gels, patches, oral tablets, injections, or topical solutions, the bioidentical testosterone is absorbed into the bloodstream where it circulates throughout the body, raising testosterone to optimal levels for a man’s age.
This replaces the testosterone that the body is no longer producing on its own due to aging, helping to reduce symptoms of low testosterone like low energy, reduced sex drive and function, mood changes, and muscle loss. BHRT provides you with a customized long-term treatment to achieve normal, healthy testosterone levels and alleviate issues caused by testosterone deficiency.
Health Impacts of BHRT
BHRT may also provide some benefits by replacing hormones that decline with menopause. Potential benefits when using BHRT include:
- Improvement in mood
- Quality of life
- Sexual function
- Sleep Quality
- Vaginal health
Health Risks and Adverse Effects
However, BHRT is not without risks and side effects that should be considered. Here are some of the possible adverse effects of BHRT when not administered properly.
In women
BHRT can increase the risk of developing blood clots as estrogen therapy elevates certain clotting factors in the blood. This increases the risk for women to develop dangerous conditions like venous thromboembolism and stroke.
BHRT-containing progesterone can also increase the risk of endometrial cancer if taken without progesterone by potentially stimulating the endometrium.
In men
The synthetic estrogen in BHRT works against the body’s natural production of testosterone, which can lead to decreased libido and muscle mass as well as fatigue and hair loss over time.
Importance of Regular Blood Tests
A thorough health history and physical examination before starting BHRT is paramount to the success of the treatment — this includes blood tests.
Regular blood tests, including blood cell count and hormone levels, are important for several reasons:
- Detection of underlying health conditions: Blood tests can help detect various health conditions, such as anemia, infections, autoimmune disorders, bone marrow disorders, and cancer. This is very helpful in weighing the potential benefits of BHRT against the health risks.
- Monitoring treatment effectiveness: Blood tests can assess how well treatments are working, such as monitoring the response to medications or evaluating the progress of a disease.
- Prevention and early intervention: Regular blood tests can help identify potential health problems before symptoms manifest, allowing for early intervention and treatment.
- Tracking overall health and well-being: Routine blood testing provides a baseline for comparison over time, allowing individuals to monitor changes in their health and make informed decisions about their well-being.
- Personalized healthcare: Blood tests provide valuable information that can guide personalized healthcare decisions. This can help you and your physician to tailor your treatment according to your long-term health goals.
Conclusion
BHRT provides a personalized treatment plan that may help relieve issues related to declining testosterone. However, finding the ideal therapy demands expert oversight and supervision to ensure risk-free and impactful results.
If you want to explore bioidentical testosterone replacement therapy further, consult our knowledgeable physicians at Physicians Rejuvenation Centers. Our seasoned practitioners will examine your unique situation, craft a customized hormone therapy regimen just for you, and monitor your progress to back your wellness and health as the years pass.
Rather than quietly endure bothersome symptoms, reach out to Physicians Rejuvenation Centers today to discuss potential solutions. You can also call us at 561-783-5153 for a quicker conversation! Speaking with us is the first step to feeling like yourself again.